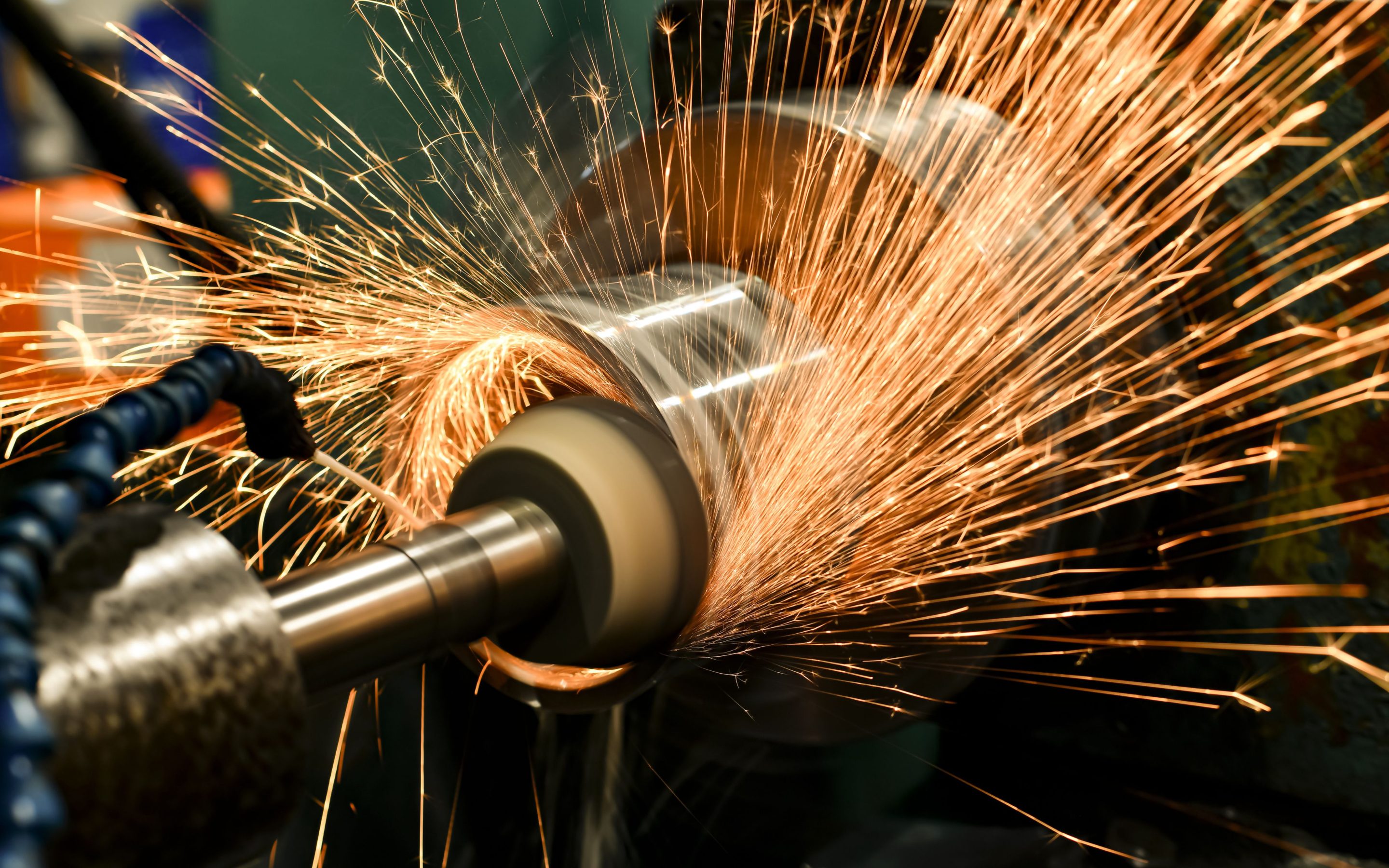
Curious about abrasive wheels and their diverse applications? Whether you’re involved in metalworking, construction, manufacturing or even just home DIY, understanding these tools is vital for safe and effective usage.
As a trusted UK health and safety advisory, we at Safety Services Direct are sharing our guide to abrasive wheels, covering everything from their types and applications to crucial safety measures. So, if you’ve ever wondered about grinding, cutting, flap, or wire brush wheels, you’re in the right place. Let’s explore these tools and ensure you and your team understand them for secure handling and optimal performance.
What are Abrasive Wheels?
Abrasive wheels are tools designed for material removal through abrasive action. There are several different types of abrasive wheels, which are used for diverse purposes, including metal cutting, surface preparation, and precision grinding. Their versatility makes them crucial in tasks ranging from fabricating components to refining surfaces in construction projects.
Types of Abrasive Wheels
There are plenty of abrasive wheels, which are split up into four distinct categories. Here’s everything you need to know about these abrasive wheel categories and the options that fall within them:
Grinding Wheels
A grinding wheel is an abrasive wheel designed for precision material removal. They also come in various types, each tailored for specific applications, such as surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, and tool sharpening.
Choosing the right type of grinding wheel for your application and desired result is crucial. Here are some common types of grinding wheels and what they’re used for:
- Straight Grinding Wheels: A straight wheel is the most common type of grinding wheel, used for peripheral grinding.
- Cylinder or Wheel Ring Grinding Wheels: These wheels are mainly used in vertical spindle grinders for cylindrical surfaces, such as the outside of a cylinder, rod, or tube.
- Tapered Grinding Wheels: Tapered wheels are used for grinding threads, gear teeth, and other similar applications.
- Straight Cup Grinding Wheels: A straight cup wheel has a slightly tapered face and is used for peripheral and face grinding.
- Dish Grinding Wheels: Dish wheels are used for grinding flat surfaces. They may have a very slight concavity, which helps maintain flatness and prevent the burning of the workpiece.
- Diamond Wheels: Diamond wheels are suitable for grinding hard materials such as carbides, ceramics, and glass. They offer high precision and excellent wear resistance.
- CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) Wheels: CBN wheels are similar to diamond wheels but are specifically designed for grinding ferrous materials. They provide high hardness and thermal conductivity.
- Mounted Points: These are small, specialised grinding wheels mounted on a spindle for precision applications in areas that are difficult to reach with larger wheels.
- Cut-off Wheels: Also known as thin wheels, these are used for cutting rather than grinding. They are designed for precision cutting metal, alloys, and other materials.
- Flaring Cup Grinding Wheels: These wheels have a larger contact area, making them suitable for heavy-duty grinding and contouring.
- Internal Grinding Wheels: Internal grinding wheels are used for grinding the inner surfaces of holes or bores.
- Rubber Bonded Wheels: These wheels use a rubber bond for softer grinding applications, such as finishing and polishing.
- Resinoid Bonded Wheels: Resin-bonded wheels are versatile and can be used for various applications. They are suitable for precision grinding and cutting.
- Metal Bonded Wheels: Metal-bonded wheels are often used for grinding hard materials and provide high durability.
- Grinding Segments: These are large blocks or sections of abrasive grains used for surface grinding.
Cutting Wheels
Cutting wheels, also known as cut-off wheels or abrasive disks, are specialised for slicing through materials, typically at narrow, precise 90-degree angles. This makes them indispensable in tasks requiring precision cuts and incisions.
The key considerations when choosing a cutting wheel include the material being cut, the desired cut quality, and the tool or machine being used. Here are some common types of cutting wheels and their uses:
- Type 1 Straight Wheels: These are flat, thin-cutting wheels without a depressed centre. They are used for cutting on the edge or periphery of the wheel.
- Type 41 Depressed Center Wheels: Also known as flat cut-off wheels, these have a depressed centre to allow for cutting at various angles. They are commonly used in angle grinders.
- Type 42 Depressed Center Cutting Wheels: These are similar to Type 41 but with a thicker cross-section. They are suitable for heavier-duty cutting applications.
- Type 27 Depressed Center Grinding Wheels: These are designed for blending, grinding, and cutting. Their depressed centre allows for multiple applications with the same wheel.
- Type 28 Depressed Center Grinding Wheels: These are similar to Type 27 wheels but with a steeper angle for better surface contact. They are also known as saucer wheels and are most often used for aggressive material removal.
- High-Speed Reinforced Cut-Off Wheels: These cutting wheels are reinforced with fibreglass to withstand higher rotational speeds. They are suitable for high-speed tools.
- Metal Cutting Wheels: Specifically designed for cutting metal, these wheels may have a unique formulation to handle the hardness and toughness of metal materials.
- Masonry Cutting Wheels: These wheels are designed for cutting through masonry materials like concrete, brick, and stone. They have a different abrasive composition to handle the hardness of these materials.
- Tile Cutting Wheels: Specially designed for cutting tiles and ceramics, these provide clean cuts without chipping the material.
- Diamond Cutting Wheels: Used for cutting hard materials such as concrete, ceramic, and metal. Diamond cutting wheels have diamond particles embedded in the abrasive matrix for enhanced cutting performance.
- Abrasive Chop Saw Wheels: These wheels are designed for use with chop saws or stationary machines to cut through various materials quickly.
- Thin Cut-Off Wheels: Extremely thin wheels for precision cutting with minimal material waste; these are commonly used for sheet metal and thin metal cutting applications.
Flap Wheels
Flap wheels are made up of overlapping abrasive flaps arranged radially around a central hub. Known for their flexibility and ability to conform to irregular surfaces, they excel in finishing and polishing applications, providing a smooth, uniform result.
Here are some common types of flap wheels:
- Unmounted Flap Wheels: These are the standard flap wheels with flaps arranged radially around a central core. They are commonly used in handheld grinders or bench grinders for general-purpose applications.
- Mounted Flap Wheels: These are similar to unmounted flap wheels, but they are mounted on a shank for use in drills or die grinders. They are convenient for reaching tight or intricate areas.
- Interleaved Flap Wheels: These wheels have alternating flaps of abrasive material and non-abrasive material, providing a smoother finish. They are suitable for applications where a fine finish is crucial.
- Tapered Flap Wheels: Tapered flap wheels have flaps arranged in a conical shape, making them ideal for contouring and reaching into tight spaces. They are commonly used in metal fabrication for shaping and finishing.
- Flap Brushes: Instead of rigid flaps, flap brushes have flexible bristles impregnated with abrasive particles. They are suitable for light deburring, cleaning, and surface preparation.
- Flap Wheels with Shank: These wheels have a shank attached for use in drills or other rotary tools. They are convenient for precision work and accessing hard-to-reach areas.
- Spindle Mounted Flap Wheels: Similar to flap wheels with shanks, these are designed to be mounted directly on a spindle for polishing and finishing applications.
- Flap Wheels with Keyway: These flap wheels have a keyway on the hub, allowing them to be securely mounted on specific tools and ensuring proper alignment during use.
- Flap Wheels with Grooves: Some flap wheels feature grooves on the flaps, providing additional flexibility and conformability. They are suitable for irregular surfaces and contours.
- Flap Wheels with Coated Abrasive Flaps: Flap wheels can have coated abrasive flaps, such as aluminium oxide or zirconia, for enhanced durability and cutting performance. They are suitable for aggressive material removal.
- Non-Woven Flap Wheels: Instead of traditional abrasive flaps, non-woven flap wheels use non-woven abrasive material. They are ideal for light deburring, cleaning, and blending without scratching the workpiece.
Wire Brush Wheels
Wire brush wheels, also known as wire wheels, are used for various cleaning, deburring, and surface preparation applications. They efficiently remove rust, paint, and other surface contaminants, making them invaluable in metal preparation.
The types of wire brush wheels vary based on their design, bristle material, and intended use. Here are some common types of wire brush wheels:
- Crimped Wire Wheel Brushes: These wire wheels have crimped or twisted wire bristles, providing flexibility and a softer brushing action. They are suitable for light to medium-duty applications and are commonly used for cleaning and deburring.
- Knot Wire Wheel Brushes: Knot wire wheels have twisted wire bristles with a knot-like structure, making them more rigid and aggressive. They are effective for heavy-duty applications, such as removing rust, scale, and weld spatter.
- Stringer Bead Wire Wheel Brushes: These brushes have narrow face widths, making them suitable for cleaning and deburring in tight spaces, such as weld joints and seams.
- Cup Wire Brushes: Cup brushes have a cup-shaped design with wire bristles arranged in a circular pattern. They effectively remove rust, paint, and corrosion from flat surfaces.
- Wheel Wire Brushes: Wheel brushes are similar to cup brushes but have a flat profile. They are suitable for cleaning larger flat surfaces.
- End Brush Wire Wheels: End brushes have a small, pointed design for precision work, such as cleaning corners, edges, and hard-to-reach areas.
- Wire Wheel with Arbor Hole: These wires are designed to be mounted on a bench grinder or other power tools using an arbor or spindle. They are versatile and can be used for various applications.
- Twisted-in-Wire Brushes: Twisted-in-wire brushes consist of wire bristles twisted into a wire stem. They are used for manual cleaning and come in various shapes and sizes for different applications.
- Stainless Steel Wire Brushes: Wire brushes made from stainless steel bristles are resistant to corrosion and are suitable for applications where contamination is a concern.
- Brass Wire Brushes: Brass wire brushes are softer than steel brushes and are commonly used for cleaning softer materials, such as copper or aluminium, without causing damage.
- Nylon Wire Brushes: Nylon brushes are non-metallic and are used for applications requiring softer brushing, such as cleaning delicate surfaces or removing paint without scratching.
- Carbon Steel Wire Brushes: Carbon steel wire brushes are durable and suitable for various applications, including rust and paint removal.
Abrasive Wheel Safety
Abrasive wheels are undoubtedly dangerous if not used carefully. This is why Safety Services Direct offers a comprehensive online abrasive wheel training course to ensure that all employees understand the proper storage, handling, and usage of abrasive wheels. Understanding maximum RPM, adhering to guidelines for mounting, and using appropriate safety gear is crucial to preventing accidents and injuries.
To find out more about our safety course or to query our other health and safety services, contact us today at 0121 348 7828.